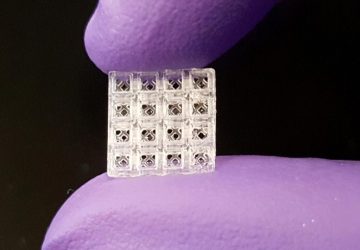
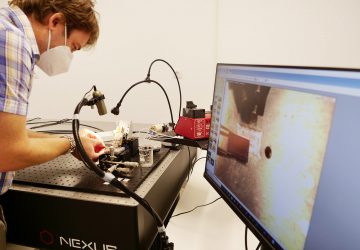
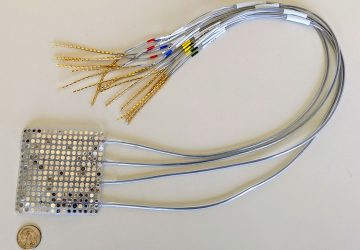
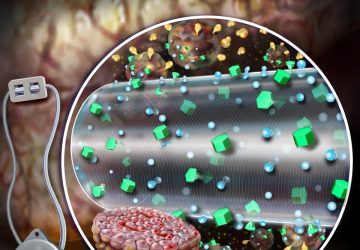
In a pandemic, quick at-home testing is essential not just for isolating cases but also for compiling big picture data. When COVID-19 struck, however, all the common rapid testing formats were laborious to use and tough for non-specialists to interpret. So Professor Sam Sia, an expert in point-of-care diagnostics and therapeutics, decided to pivot his research to address the crisis. Sia’s lab has spent the past few months developing simple…
Read MoreElectronic Blood Vessels to the Rescue
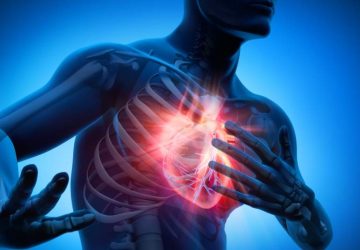
Hybrid natural-artificial blood vessels could also enable gene therapies and drug delivery The number one cause of mortality worldwide is cardiovascular disease. Now scientists reveal electronic blood vessels might one day use electricity to stimulate healing and deliver gene therapies to help treat such maladies, a new study finds. One-third of all U.S. deaths are linked to cardiovascular disease, according to the American Heart Association. When replacement blood vessels are…
Read MorePitt team receives NIH award to optimize tissue-engineered vascular graft design
Just as a climbing plant needs the right trellis to thrive, a small-diameter tissue-engineered vascular graft (TEVG) needs the right scaffold to transform seeded cells into a native-like artery that can save a life. A team led by the University of Pittsburgh’s David A. Vorp received a $1.1M award from the National Institutes of Health to optimize this emerging technology for cardiovascular disease. They will examine the best combination(s) of…
Read MoreNew Graphene Face Masks Offer Very High Anti-bacterial Efficiency, Deactivation of Coronaviruses
Anti-bacterial efficiency close to 100% under 10-min sunlight and promising results in deactivation of coronaviruses. Face masks have become an important tool in fighting against the COVID-19 pandemic. However, improper use or disposal of masks may lead to “secondary transmission.” A research team from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has successfully produced graphene masks with an anti-bacterial efficiency of 80%, which can be enhanced to almost 100% with exposure…
Read MoreLab Tests Show Minibinder Proteins Are as Effective as Antibodies at Blocking SARS-CoV-2
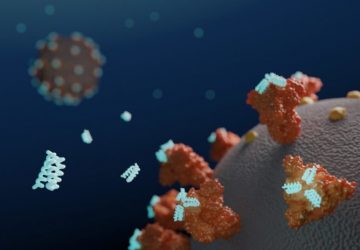
Researchers at the University of Washington (UW) School of Medicine Institute for Protein Design have used computers to design small proteins, or minibinders, that bind tightly to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein and prevent it from infecting cells. Their work has resulted in the development of a lead antiviral candidate, LCB1, which is currently undergoing evaluation in rodents, and which appears to rival the most effective known SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies in…
Read MoreRobotics, AI, and Cloud Computing Combine to Supercharge Chemical and Drug Synthesis
IBM looks to revolutionize industrial chemistry and in the process may have cut the discovery time for Covid-19 treatments in half IBM must be brimming with confidence about its new automated system for performing chemical synthesis because Big Blue just had twenty or so journalists demo the complex technology live in a virtual room. IBM even had one of the journalists choose the molecule for the demo: a molecule in a…
Read MoreNew “Cyborg” Technology Could Enable Merger of Humans and AI
Although true “cyborgs” — part human, part robotic beings — are science fiction, researchers are taking steps toward integrating electronics with the body. Such devices could monitor for tumor development or stand in for damaged tissues. But connecting electronics directly to human tissues in the body is a huge challenge. Now, a team is reporting new coatings for components that could help them more easily fit into this environment. The…
Read MoreCOVID-19 Coronavirus Breathalyzer Test Developed
Few people who have undergone nasopharyngeal swabs for coronavirus testing would describe it as a pleasant experience. The procedure involves sticking a long swab up the nose to collect a sample from the back of the nose and throat, which is then analyzed for SARS-CoV-2 RNA by the reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Now, researchers reporting in ACS Nano have developed a prototype device that non-invasively detected COVID-19 in the…
Read MoreLEGO-Inspired 3D-Printed Bricks Help Broken Bones Heal Faster
Hollow, flea-sized blocks can be filled with materials that improve healing. Tiny, 3D-printed bricks have been designed to heal broken bones — and could one day lead to lab-made organs for human transplant. Inspired by Lego blocks, the small, hollow bricks serve as scaffolding onto which both hard and soft tissue can regrow better than today’s standard regeneration methods, according to new research published in Advanced Materials on July 23,…
Read MoreMembrane nanoparticles acts as a bait to trap SARS-CoV-2
In an exciting new bioRxiv* preprint research paper, Chinese researchers describe the development of membrane nanoparticles from ACE2-rich cells with a potent capacity to block the adherence of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The relentless coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic quickly prompted the pursuit of novel effective therapeutic agents against the highly virulent SARS-CoV-2 virus. One of the prime targets for researchers is the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), the…
Read More