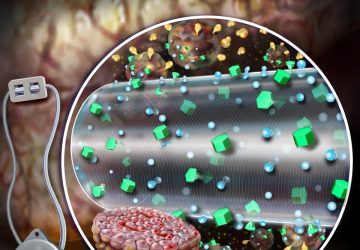
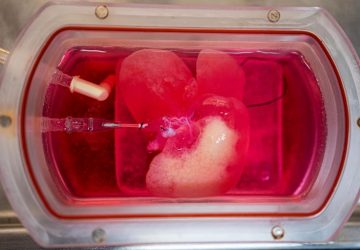
Bioprinting could happen via minimally invasive surgery Right now, almost 70,000 people in the United States alone are on active waiting lists for organ donations. The dream of bio-printing is that one day, instead of waiting for a donor, a patient could receive, say, a kidney assembled on demand from living cells using 3-D printing techniques. But one problem with this dream is that bio-printing an organ outside the body necessarily…
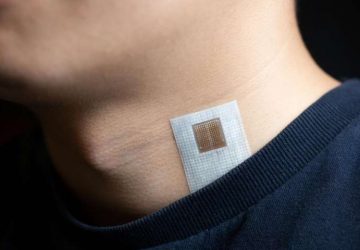
Read MoreSticker-Like Medical Device Offers Continuous Monitoring for COVID-19
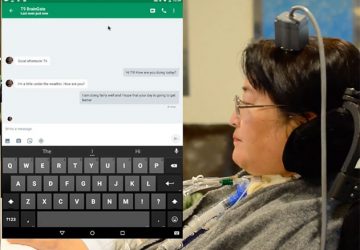
Clinical-grade wearable streams symptom data to physicians. Stamp-sized device comprises a suite of clinical-grade sensors, including temperature and pulse oximetry Device sits at the base of the throat to pick up vibratory signatures of breathing, coughing, swallowing Since developing the device, researchers have tested it on more than 50 physicians, rehabilitation specialists and patients at Shirley Ryan AbilityLab and Northwestern Memorial Hospital Researcher: ‘We are already seeing clear vital sign…
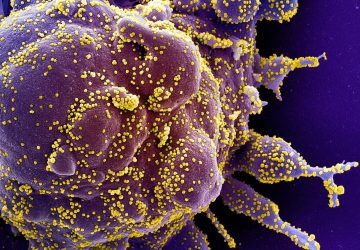
Read MoreLive attenuated vaccines may prevent lung inflammation and sepsis associated with COVID-19
A paper published by Paul Fidel, Jr., PhD, Professor and Director of the Center of Excellence in Oral and Craniofacial Biology and Associate Dean for Research at LSU Health New Orleans School of Dentistry, and Mairi Noverr, PhD, Professor of Microbiology & Immunology at Tulane University School of Medicine in New Orleans, suggests that live attenuated vaccines such as MMR (measles, mumps and rubella) may prevent the severe lung inflammation…
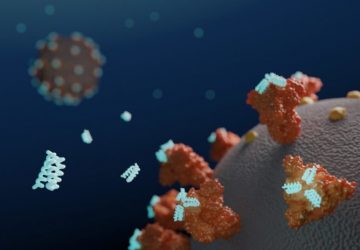
Read MoreMIT Researchers Design Experimental Peptide That Targets and Destroys COVID-19
Computational modeling yields a protein fragment that could bind to coronavirus spike proteins and destroy them. The research described in this article has been published on a preprint server but has not yet been peer-reviewed by scientific or medical experts. Using computational models of protein interactions, researchers at the MIT Media Lab and Center for Bits and Atoms have designed a peptide that can bind to coronavirus proteins and shuttle…
Read MoreCan Sensors That Detect Coronavirus in the Air Help Economies Reopen Safely?
Several companies are selling devices that detect the novel coronavirus, but none give instant readings As businesses scramble to find ways to make workers and customers feel safe about entering enclosed spaces during a pandemic, several companies have proposed a solution: COVID-19 air monitoring devices. These devices suck in large quantities of air and trap aerosolized virus particles and anything else that’s present. The contents are then tested for the presence of the novel…
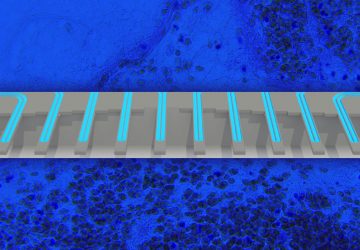
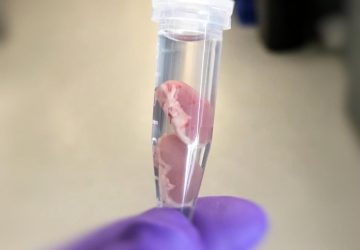
Read MoreMini Human Livers Grown in Lab Successfully Transplanted Into Rats
Using skin cells from human volunteers, researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine have created fully functional mini livers, which they then transplanted into rats. In this proof-of-concept experiment, the lab-made organs survived for four days inside their animal hosts. These results were published today (June 2, 2020) in Cell Reports. “Seeing that little human organ there inside the animal – brown, looking like a liver – that…
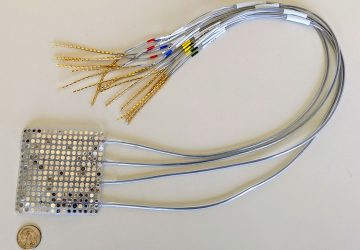
Read MoreResearchers Can Now Interrogate Body-on-Chip
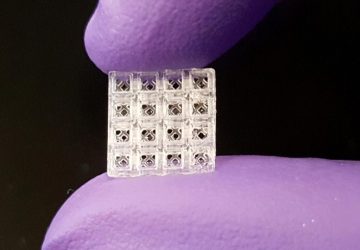
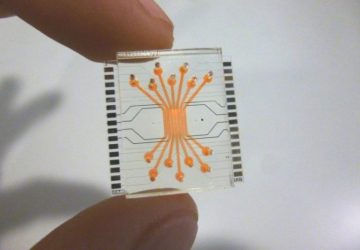
The Interrogator system links ten organs-on-chips to predict how a human body metabolizes drugs Scientists have just announced the completion of an eight-year-long project to integrate 10 human organs-on-chips in an automated system to study how drugs work in the body. The technology provides an alternative to testing drugs on humans or other animals. Referred to as the “Interrogator” by its developers, the system links up to ten different human organ chips—miniaturized…
Read MoreWearable Patch Uses Machine Learning to Detect Sleep Apnea
A new device could make it easier to monitor sleep apnea at home Getting screened for sleep apnea often means spending a night in a special clinic hooked up to sensors that measure your brain activity, eye movement, and blood oxygen levels. But for long-term, more convenient monitoring of sleep apnea, a team of researchers has developed a wearable device that tracks a user’s breathing. The device, described in a study…
Read MoreModified cancer drug effective against multi-resistant bacteria
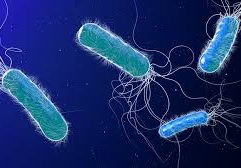
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria are increasingly the source of deadly infections. Scientists have now modified an approved cancer drug to develop an active agent against multidrug-resistant pathogens. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria are increasingly the source of deadly infections. A team of scientists from the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and the Helmholtz Center for Infection Research (HZI) in Braunschweig have now modified an approved cancer drug to develop an active agent against multidrug-resistant pathogens….
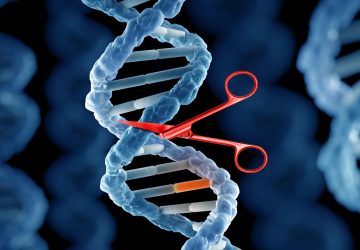
Read MoreDARPA Seeks Pathogen Detectors That Use CRISPR to Run 1,000 Tests at Once
DARPA is asking researchers to use gene-editing technologies for portable diagnostics that produce results in 15 minutes The U.S. Department of Defense has put out a call to researchers to develop devices that detect pathogenic threats by performing up to 1,000 diagnostic tests in fewer than 15 minutes. The devices ideally would determine the presence of a pathogen, and useful details about it, such as whether it’s a drug resistant variety, the…
Read More